🔬 Analysis Report
Original Image
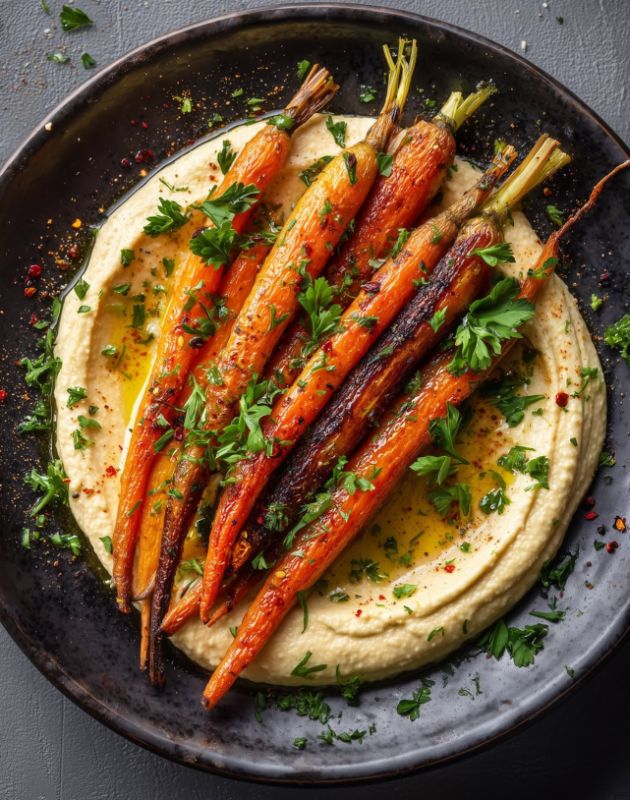
AI-Generated Analysis
✔️ Vegetarian Suitability
The dish appears to contain only plant-based ingredients (carrots, hummus, herbs). Hummus is made from chickpeas, tahini (sesame seed paste), olive oil, lemon juice, and garlic. There are no visible or expected ingredients derived from animal slaughter. Dairy (milk, cheese, whey, cream, butter) are allowed in the 'vegetarian' diet as per the instructions.
Confidence: High
🎯 Targeted Health Analysis
❤️ Cholesterol & Heart Health
This dish can be heart-healthy depending on the preparation methods. The carrots themselves are low in cholesterol and fat. The hummus contributes fiber and healthy fats, which can be beneficial for heart health. However, the amount and type of oil used for roasting the carrots and the fat content of the hummus (especially saturated fat if it contains excessive tahini or added oils) will significantly impact its heart-healthiness. High sodium content in the hummus would also be a concern.
Recommendation: Consider a healthier version. Limit the amount of oil used for roasting the carrots and choose or prepare low-sodium, low-saturated-fat hummus.
🧂 Sodium & Blood Pressure
The sodium content of the hummus is the primary concern regarding blood pressure. Commercial hummus can be very high in sodium. Roasting the carrots generally does not add significant sodium unless salt is added during the process. The overall sodium content depends heavily on the hummus recipe or brand. The added spices could also contain sodium.
Recommendation: Choose a low-sodium hummus variety or make your own to control the sodium content. Be mindful of added salt when roasting the carrots.
Food Item Identified: Roasted carrots with hummus and herbs.
General Health Assessment: This dish appears to be a healthy option, rich in vitamins and fiber. Carrots provide beta-carotene, while hummus offers protein and fiber. The dish's overall healthiness depends on the amount of oil used in roasting the carrots and the sodium content of the hummus.
⚠️ Important Warnings
Potential Allergen (Hummus (Sesame)): Hummus contains sesame (tahini), a common allergen. Individuals with sesame allergies should avoid this dish. (High)
Common Visible Components Analysis
Carrots
General Contribution: Provides vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
Common Benefits:
- 👍 Rich in beta-carotene, beneficial for eye health.
- 👍 Good source of fiber, aiding digestion.
- 👍 Contains antioxidants.
Common Drawbacks:
- 👎 High in natural sugars, though the overall glycemic load is moderate.
- 👎 Roasting may reduce some nutrient content depending on temperature and duration.
Hummus
General Contribution: Provides protein, fiber, and healthy fats.
Common Benefits:
- 👍 Source of plant-based protein.
- 👍 Rich in fiber, promoting satiety and digestive health.
- 👍 Contains healthy fats from tahini and olive oil.
Common Drawbacks:
- 👎 Can be high in sodium, depending on the preparation.
- 👎 May contain added oils, increasing the calorie content.
Herbs (Parsley)
General Contribution: Adds flavor and some vitamins.
Common Benefits:
- 👍 Source of vitamins A, C, and K.
- 👍 Adds antioxidants.
- 👍 Enhances flavor without adding calories.
Common Drawbacks:
- 👎 Minimal nutritional impact due to small quantity.
❓ What Cannot Be Determined From Photo:
- • The specific ingredients in the hummus are unknown, so sodium and fat content cannot be accurately assessed.
- • The type of oil used for roasting the carrots is unknown.
- • The specific seasonings used are unknown, potentially impacting sodium and other micronutrient levels.
💡 Suggestions & Healthier Alternatives:
- • Use minimal oil when roasting the carrots, or consider steaming them instead.
- • Choose a low-sodium hummus variety, or make your own to control the sodium content.
- • Add other vegetables, such as bell peppers or cucumbers, for added nutrients and variety.
- • If making at home, add lemon juice to help cut the bitterness of the carrots